Embarking on your game development journey with Unity? Grasping foundational programming concepts like Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and the Model-View-Controller (MVC) design pattern can significantly enhance your development process❗
🧱 What is Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)?
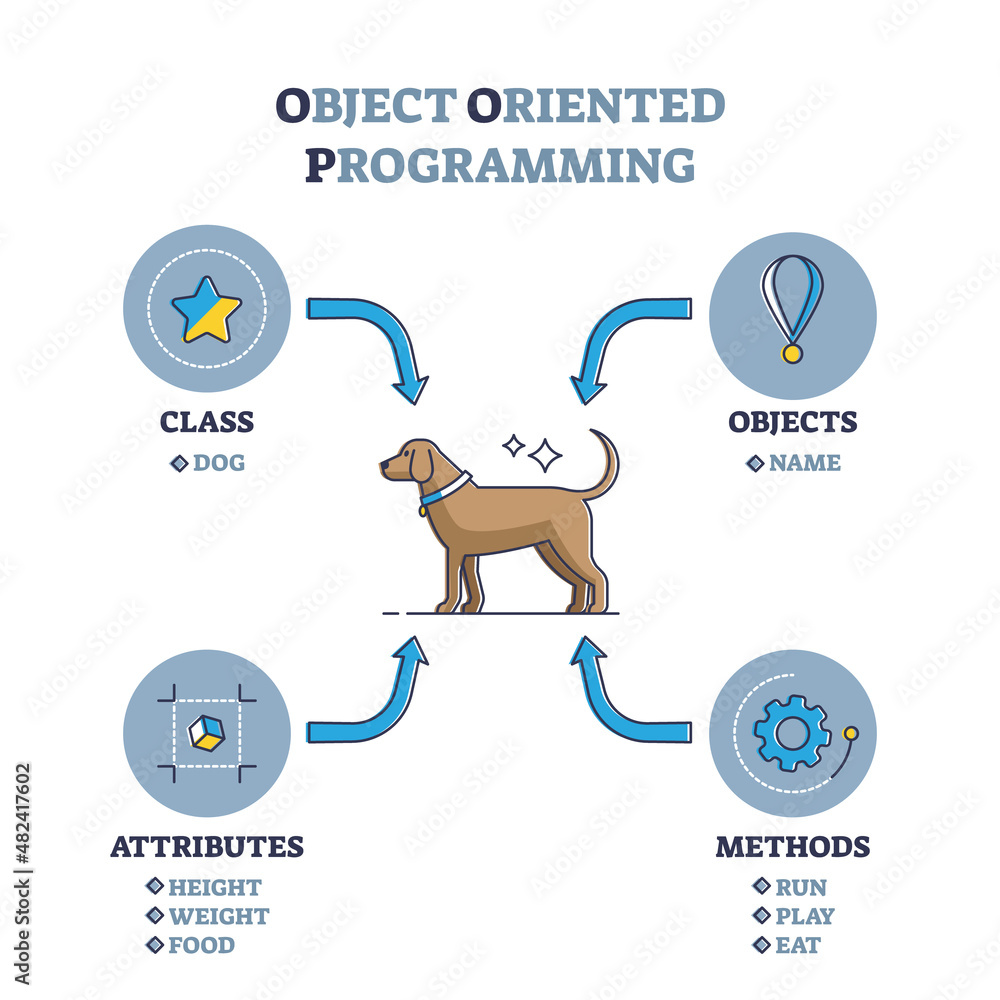
Object-Oriented Programming is a paradigm that structures software design around objects—entities that encapsulate data and behaviors. This approach promotes code reusability, scalability, and maintainability.
Core Principles of OOP:
- Encapsulation: Bundling data and methods that operate on that data within one unit, e.g., a class;
- Inheritance: Creating new classes that inherit attributes and behaviors from existing classes;
- Polymorphism: Allowing entities to be represented in multiple forms, enabling flexibility in code;
- Abstraction: Hiding complex implementation details and showing only the necessary features of an object.
In Unity, OOP is utilized through C# scripting, where you define classes for game objects, behaviors, and systems. In my case, the current project structure looks like this:
🧭 Introducing the Model-View-Controller (MVC) Pattern:
MVC is a software architectural pattern that separates an application into three interconnected components:
- Model: Manages the data and business logic;
- View: Handles the presentation layer and user interface;
- Controller: Processes user input and interacts with the Model.
This separation facilitates organized code, making it easier to manage and scale your application.
For an in-depth exploration of implementing MVC in Unity, consider reading this article:
👉 Unity with MVC: How to Level Up Your Game Development
🛠️ Applying OOP and MVC in Unity:
To solidify your understanding, consider creating a simple Unity project that implements these concepts:
- Model: Define a
PlayerModelclass that holds player data like health and score; - View: Create a
PlayerViewscript that updates the UI elements based on thePlayerModeldata; - Controller: Implement a
PlayerControllerscript that handles user input and updates thePlayerModeli.e. right click on mouse is adding 100 to the score.
This structure ensures a clear separation of concerns, making your code more organized and easier to maintain.
📚 Resources for Further Learning:


